Promoting a Sustainable 3D-printed Circularity with Zero-Waste Approach
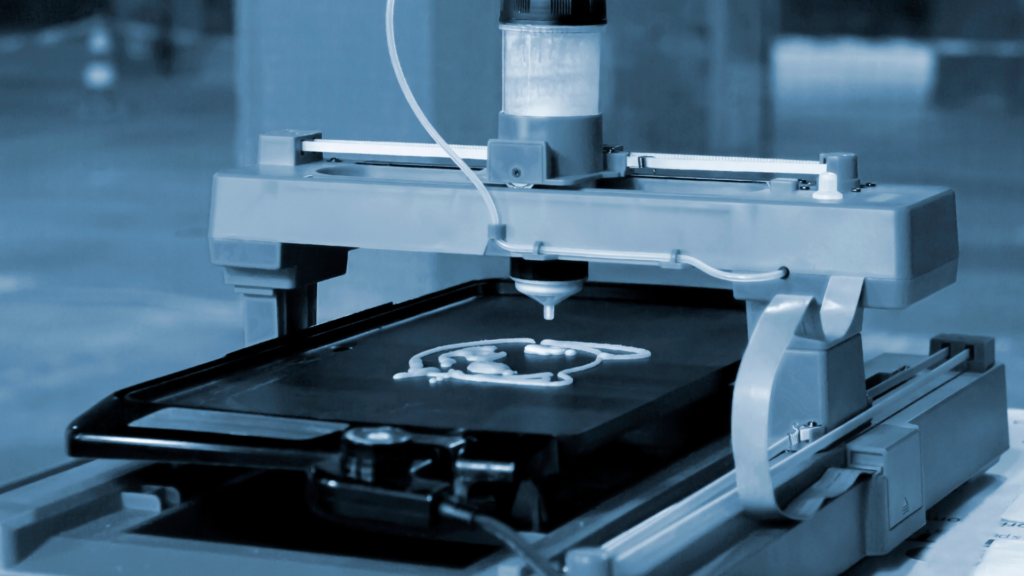

Welcome, folks, to the glorious revolution of 3D-printed construction! Imagine a world with zero waste, sustainable materials, and circularity in the construction industry. Do you think it’s too good to be true? Well, hold on to your hats because this isn’t just a pie in the sky idea; it’s a reality that’s poised to change how we build our future! In this easy-to-read article, we’ll be talking about how to create circularity in 3D-printed construction, focusing on utilizing sustainable materials and minimizing waste. Say goodbye to traditional ways fraught with needless waste and say hello to precision and potential for green, sustainable construction. Roll up your sleeves, as we’re about to deep-dive into sustainable materials, waste minimization, design optimization for circularity, and oh so much more!
Understanding the Need for Circularity in 3D-Printed Construction
The world of construction has been going down a rocky road. Now, here’s the ugly truth: traditional building methods are creating a massive mountain of waste. It’s high time we find a better way to build our future. And guess what? The answer might just be in 3D-printed construction.
Challenges of Traditional Construction
Let’s face it; traditional construction methods have a dirty little secret: they’re pretty wasteful. It’s common to see leftover materials and debris, transforming the site into a deserted field after the final brick has been laid.
Excessive Waste Production
The old ways of building have us ordering more materials than needed, just in case. Stockpiling, overspending, and eventually tossing wasted materials into a growing pile of termination. We spend more and waste even more, it’s like pouring money down the drain!
Limited Sustainability
Moreover, how sustainable are these traditional materials? We are stripping our planet bare, creating a future as concrete and cold as the materials we use.
The Role of 3D Printing in Construction
Here’s where things start to get exciting. What if I told you, there’s a way to construct more sustainably without sacrificing efficiency or quality? Welcome to the future: 3D-printed construction.
Precision and Efficiency
Imagine a construction method so precise, excess materials are virtually eliminated. It’s all about creating just what you need and nothing more. It’s possible with 3D printing. Controlled down to the last pixel, 3D printed structures are as accurate as they come.
Potential for Sustainability
And what about sustainability? How’s 3D-printed construction faring in that department? Well, I’m glad you asked. With 3D printing, builders can choose materials more considerately. Plastics, metals, and even glasses can all be recycled and returned to the construction cycle.
When it comes to construction, the future truly is 3D. Together, let’s create a world that prioritizes circularity, minimizes waste, and serves us sustainably in the long run.
Utilizing Sustainable Materials in 3D-Printed Construction
When it comes to 3D-printed construction, the materials we choose to use can make a monumental difference to our environment. So, let’s talk about how we can pioneer change by utilizing more sustainable materials in our work.
Types of Sustainable Materials
We’ve got a buffet of options when it comes to choosing sustainable resources. And guess what? Some of these materials are already lying around, waiting to be put to good use.
Recycled Concrete and Glass
Think about all that concrete and glass we toss out. We can breathe new life into these materials. Recycled concrete and glass are not only plentiful, but they’re mighty powerful when reinforced properly. They stand strong against the elements, making them ideal candidates for sustainable construction.
Bioplastics and Natural Fibers
In the world of 3D printing, bioplastics and natural fibers are taking the spotlight. Derived from natural sources like plants, waste, and even bugs, these materials sit on the more eco-friendly side of the scale. Imagine creating buildings from materials bestowed to us by Mother Nature herself!
Upcycled Materials
Now, let’s switch gears to upcycled materials. These are items that were destined for the landfill but are instead transformed into something new. Stuff like plastic bottles, old car parts, and even scrap metal can be upcycled and fused into the 3D printing process.
Strategies for Local Sourcing
Utilizing sustainable materials is one facet of this sparkling diamond of circularity. Another crucial aspect lies in local sourcing.
Low-Impact Cement Alternatives
We all know that the production process of traditional cement isn’t exactly green or friendly to our environment. Hence, exploring low-impact cement alternatives becomes very critical. Things like green concrete made from recycled materials or geopolymers using industrial waste are not only locally sourced but also have a substantially lower carbon footprint.
By combining sustainable materials and clever local sourcing, we can revolutionize the concept of 3D-printed construction and make it a more welcoming arena for Mother Nature.
Minimizing Waste in the 3D-Printed Construction Supply Chain
Oh boy, time to give the old ways the boot! See, traditional construction builds a lot of waste. But 3D-printed construction? That’s a horse of a different color. It’s all about precision, efficiency, and most importantly—cutting way down on waste! Here’s how we do it:
Design Optimization
Let’s kick off with design optimization. Picture a sculptor, shaping a masterpiece from a lump of clay, chiseling away until it’s just right. That’s what we’re talking about here, folks.
Precision Printing Techniques
Precision printing techniques are your trusty chisel in this process. Instead of rough-housing your materials, a 3D printer cuts out your design exactly as you need it—down to the millimeter. No more, no less. That means we’re using less raw material to begin with. And less stuff out of the ground means less waste at the end. Cool, huh?
On-Demand Production
But this ain’t just about precision. On-Demand production has a vital part to play. You only print what you need when you need it. Got a sudden change in the design? No problem! Just tweak the model and print. No need to throw away piles of unused materials because of last-minute changes.
Utilizing In-Situ Recycling
Next up, we’ve got in-situ recycling. And this, my friends, is where the magic really happens!
Closed-Loop Material Systems
Imagine a world where your waste doesn’t just disappear. It goes back into the same process to create something new. Enter stage left, closed-loop material systems. These systems collect the waste, breaks it down, and feed it right back into the printer. We’re talking a serious game-changer in reducing waste in construction.
Upcycling Methods
Don’t think we’ve forgotten about recycling’s hip younger cousin—upcycling. In a nutshell, upcycling methods are about taking something that’s destined for the trash heap and turning it into a valuable resource. It’s about creative problem-solving, taking that so-called waste and making it useful again in the construction process.
So, when you get right down to it, minimizing waste in 3D-printed construction isn’t just a pipe dream. It’s a reality. And it’s one that’s making our industry smarter, more sustainable, and—dare I say it?—a whole lot more exciting. We’re making waste a thing of the past, one 3D-printed structure at a time. How’s that for a bold, new future? Vote for the future, vote for 3D-printed construction!
Innovative Design for Circularity
In our quest to create circularity in 3D-printed construction, design plays a crucial role. Innovative design strategies can go a long way in ensuring sustainability and minimizing waste. How, you ask? Let’s dive in.
Implementing Parametric Design
In the world of 3D-printed construction, parametric design is the new kid on the block. But trust me, this kid’s got some cool tricks up his sleeve. Parametric design revolves around setting certain parameters and rules for the design process. These could be related to material utilization, environmental factors, or construction techniques. Once you’ve got these rules in place, the design automatically adjusts to meet them.
Now, before you start scratching your heads and asking Mr. Google about parametric design, let’s talk about another significant aspect- Design for Disassembly (DfD).
Design for Disassembly (DfD)
Aren’t we all a little guilty of forgetting about our constructions once they have served their purpose? DfD encourages us to plan ahead. It involves designing in such a way that structures can be easily disassembled at the end of their life cycle. The materials can then be reclaimed and reused, thus making the construction process a circular one.
And while we are on the subject of implementing smart design methods, let’s not forget about the importance of Structural Optimization.
Structural Optimization
The name says it all, folks! Structural optimization is about making the most out of every bit of material that goes into construction. Whether it’s about reducing weight, maximizing strength, or improving efficiency, it’s a strategy that needs no introduction to those in favour of circular 3D-printed construction.
And speaking of efficiency and optimization, have you ever thought about the potential of Creating Modular and Lightweight Designs?
Creating Modular and Lightweight Designs
Modular designs are like the LEGO blocks of the construction world. They can be put together in any way you want, creating endless possibilities for design. What’s more, they are lightweight and easy to handle.
In the context of 3D-printed construction, creating modular and lightweight designs means less waste and more possibilities for reuse. That’s like hitting two birds with one stone, wouldn’t you say?
In a nutshell, innovative designs are vital for creating circularity in 3D-printed construction. Whether it’s implementing parametric design, considering Design for Disassembly (DfD), working towards Structural Optimization or creating Modular and Lightweight Designs, every step takes us closer to our goal of sustainable, minimal-waste construction. It’s a future we can all work towards, brick by brick, or in this case, layer by 3D-printed layer.
Harnessing Technology and Monitoring Systems
Let’s dive right into this next section where we are going to explore how technology is being used in this exciting new world of 3D-printed construction.
Integrating AI-driven Design
In a world that’s buzzing with intelligent machines, AI-driven design is taking center stage in the circular construction process. It’s like having a master architect with an incredible brain that never sleeps! By crunching numbers, analyzing materials, and making real-time adjustments, this incredible tech can optimize designs on the fly. This means that we can squeeze the best output from the least amount of materials. It’s efficient, it’s smart, and it’s just downright cool!
Utilizing Blockchain for Traceability
Next on our journey through technology is blockchain. Now, I know what you’re thinking. “Isn’t that something to do with Bitcoin?” Well, you’re right, but blockchain has come a long way from being just a platform for cryptocurrency. In the realm of 3D-printed construction, blockchain is being used to establish a powerful system of traceability. It’s like having an unbreakable chain that connects each stage of the construction process, providing a transparent and trustworthy system. This transparency is vital in ensuring the circularity of the supply chain, tracing materials right back to their source.
Smart Monitoring with IoT Sensors
Onto our third tech superstar – Internet of Things (IoT) sensors. These handy little gadgets keep a close eye on the printing process, providing valuable feedback and data that can be used to monitor efficiency and pinpoint areas for improvement. Smart monitoring also helps reduce waste by identifying any discrepancies before they cause a problem.
Digital Twin Technology
Under the IoT umbrella, we have digital twin technology. It creates a virtual replica of the physical setup. This twin can simulate the production process under different scenarios. Like a dress rehearsal, we can identify potential pitfalls and fix them without wasting any physical resources.
Predictive Maintenance
Finally, let’s talk about predictive maintenance. Imagine you’re on a road trip; wouldn’t it be great if your car could warn you before it’s about to break down? That’s predictive maintenance in a nutshell! By predicting equipment failure, a potential disaster can be averted, ensuring our 3D printers are in tip-top condition, producing minimal waste, and keeping the circular construction process running smooth and efficiently.
Together, these innovative technologies are reshaping the way we think of construction. They are not just creating buildings; they’re helping us rethink how we interact with materials and waste, drawing us closer to a truly circular and sustainable future!
Sustainable Energy and Production Methods
In the drive to create a circular system in 3D-printed construction, you’ll agree that one aspect that takes center stage is sustainability. To create economic value, welfare for humans, and minimal environmental impact, we must embrace sustainable energy and production methods. Aging power plants that pump out pollutants are history! Let me tell you how exciting alternatives are changing the game entirely.
Adopting Low-Energy Printing
Traditional construction methods are energy hogs. Enter the new hero: low-energy 3D printing. By cutting down on the amount of energy used in construction, we’re putting money back in our pockets – and curbing our carbon footprint, too! 3D printers excel at printing with extraordinary precision while consuming less power. Imagine that: top-notch accuracy and energy efficiency – all in one package!
Incorporating Renewable Energy
The benefits are like a cascade effect, folks. Once you dive into low-energy printing, it’s a mirror-image step to leapfrog towards renewable energy sources. Technology advances have made it possible for construction sites to be powered by solar, wind, and even waste biomass! Not only does this slash our harmful emissions but also saves money in the long-run. It’s not magic – it’s just clean, green, innovation!
Efficiency in Production Methods
To make the whole construction process even more sustainable – there’s more! We can apply a bunch of smart strategies that make production more efficient.
Reducing Support Materials
Ever wondered about the debris and leftover materials that litter most construction sites? With 3D printing, there’s a remarkable reduction in this type of waste. The technology allows us to use just the right amount of materials needed, eliminating the need for excess inventory and reducing the waste that winds up in landfills. Now, isn’t this a circularity champion!
In conclusion, folks, there’s a powerful trifecta at play here with low-energy printing, renewable energy incorporation, and more efficient production methods. They form the pillars of shifting 3D-printed construction to a more sustainable and circular approach. To put it in simple terms – it’s indeed an exciting era for construction!
Planning for End-of-Life and Material Recovery
One critical aspect of promoting circularity in 3D-printed construction is considering the end-of-life (EOL) stage of the buildings we create. Just as humans plan for retirement years ahead, we must also plan for a building’s post-life years in advance.
Deconstruction and Recovery
When buildings complete their lifespan, they’re often demolished and become part of the massive pile of construction waste. However, 3D-printed buildings give us the ability to dream bigger and reduce this waste!
Through careful planning and cutting-edge technology, we can deconstruct rather than demolish. Deconstruction involves taking buildings apart piece by piece. It allows us to recover and reuse valuable materials, significantly reducing waste. How’s that for a dump-less future?
Think of it as a large-scale recycling program, but for buildings!
Exploring Circular Business Models
Sticking to traditional business models will put us back in the throw-away culture. We need to adopt circular business models that keep the value of materials, components and products for as long as possible in the life cycle. And one exciting model is the Product-as-a-Service.
Product-as-a-Service
This business model is a budding star of the circular economy. In essence, instead of selling a product, companies retain ownership and offer the product’s benefits as a service. This model encourages sustainable use, maintenance, and eventual recovery of products.
Seeing a building not as a static product, but a service, shifts our perspective in fascinating ways. It allows us to think differently about the design, construction, and end-of-life of a building. It prompts owners and manufacturers to take care of their buildings better, as they’re not just assets, but services to be maintained.
End-of-life planning doesn’t mean we’re all doom and gloom. It’s about preparing for a brighter, more circular future, where every product gets a second chance, and virtually nothing goes to waste. Now that’s a circle full of opportunities!
Collaborative Efforts and Policy Implementation
Our journey through the 3D-printed construction industry’s attempts to create a circular economy doesn’t stop at the level of materials, technologies, or designs. It zooms out further to look at how all these individual pieces fit into a broader societal context. This isn’t a solo mission. Nope, it calls for concerted Collaborative Efforts and Policy Implementation.
Building Industry Partnerships
The old saying goes: “No man is an island.” And believe me, in this case, no company is either. Especially in the wild, wild west of the emerging 3D printed construction industry. Industry partnerships between construction, tech, and environmental firms can pool resources, share risks, and cross-pollinate ideas. Let’s start thinking less about being “king of the hill” and more about creating a community of builders, thinkers, and innovators.
Developing Regulatory Frameworks
Our excitement about 3D printing’s potential bump up against some harsh realities. One big roadblock? Our current building codes, zoning laws, and industry regulations. They’re as old-fashioned as a stagecoach in a car showroom. Developing Regulatory Frameworks that understand and accommodate 3D-printed construction and circular principles is vital. We need policymakers who are willing to step outside their comfort zones, and industry leaders who can paint them a picture of possibilities.
Promoting Education and Standardization
An industry that doesn’t learn is an industry that doesn’t grow. Promoting Education and Standardization may sound dull as ditch water, but it’s actually sizzling with opportunity. It includes figuring out certified training courses for 3D-printed construction skills. It means academic research into the nitty-gritty of sustainable materials and circular designs.
Public-Private Partnerships
And it’s not just the responsibility of companies or universities. Governments can – and should – get in on the action. Yes, friends, we’re talking Public-Private Partnerships. By creating spaces and opportunities for collaboration, we can stimulate innovation, fast-track developments, and make sure that the benefits of circular, 3D-printed construction don’t just end up benefiting a few.
In conclusion, this isn’t just a technical transition or an industry shift. It’s a societal shift, a new way of thinking. And like all great transformations, it starts with education, collaboration, and a whole lot of enthusiasm. Are you ready to bring circularity to the 3D-printed construction industry? Let’s roll up our sleeves and get building!
Exploring the Benefits of Circular 3D-Printed Construction
Friends, gather ’round, because today we’re venturing into the exciting terrain of circular 3D-printed construction. This emerging field not only reshapes the face of building design but also brings along a trove of benefits that could dazzle even a seasoned builder. So, buckle up and let’s explore the rewards this innovative sphere promises.
Achieving Reduced Waste and Lower Carbon Footprint
Imagine a world where construction doesn’t come at the expense of our precious environment. Fancy each brick, every beam built without piling heaps of waste or puffing clouds of carbon. Well, friends, thanks to the precise fabrication methods of 3D-printed construction, that world is no longer the stuff of dreams.
Every layer of material in a 3D-printed structure is meticulously placed, meaning we only use what’s strictly needed. Hence, the monstrous waste that usually shadows traditional construction retreats to the shadows, offering us up to a whopping 30% reduction. Now, that’s something to write home about, folks!
But the benefits don’t halt at waste reduction. By using renewable or recycled construction materials, 3D-printed building slashes its carbon emissions to a fraction, doing its bit to fight the good battle against climate change. So, it’s a win-win situation – we get our structures, Mother Nature gets to breathe easy.
Enhancing Resource Efficiency
Moving on, folks, let’s talk about efficiency. Time, as they say, is gold, and in construction, it’s almost carved in stone, pardon the pun! With traditional building methods, we waste tons of hours in labor-intensive processes.
However, 3D-printing swoops in saving the day! Automated printers humming day and night, churning out components at an unheard-of speed, and voila – buildings rise from the ground at a breathtaking pace, be it rain or shine. That’s a tick on time efficiency – yet another feather in the 3D-printed cap.
Stimulating Cost Reduction and Job Creation
And the cherry on top? The good ol’ dollar sign. Yes, folks, 3D-printing shaves costs at almost every turn. From material savings and reduced labor expenses to faster project timelines, the dollars just keep adding up. And, less waste leads to less disposal cost – so, we’re padding our pockets while we’re preserving the planet!
Now, you might wonder – with all this automation, what happens to human labor? Well, fear not. While it’s true that 3D-printing takes over many laborious tasks, it opens a wealth of new job opportunities in design, machine operation, and technology development. It’s like trading in your old pickaxe for a shiny new laptop – a step up that’s a win for our brains and our backs.
So, there you have it folks – the golden trifecta: environmental care, resource efficiency, and cost-saving with job creation. A world where we construct without destruction, build while conserving, and it all comes down to circular 3D-printed construction. Now, isn’t that a future worth working towards? Let’s get on it!
The Future of Circular 3D-Printed Construction
If you ever gazed at a towering skyscraper, or wandered through an architecturally complex building, you’ve probably wondered how those structures came to be. Enter the future: Circular 3D-Printed construction. This revolutionary technique is reshaping the way we build, promising not just innovation and efficiency, but sustainability too. Let’s peek into the crystal ball and see what the future holds, shall we?
Advanced Recycling Technologies
First up is our game changer, advanced recycling technologies. Like a phoenix rising from the ashes, old materials are born anew in 3D-printed construction. Picture this: Concrete rubble and demolished buildings, instead of wasting away in some landfill, are recycled and transformed into fresh building materials. It’s not just any transformation, mind you, but one that requires much less energy than traditional methods. Now, isn’t that a neat trick?
AI-Driven Circular Design
Next, let’s talk tech—AI-driven circular design, to be precise. Imagine a machine brain, smart as a whip, capable of designing optimal structures. Everything is taken into account – from local climate conditions to the building’s intended usage – all to create intelligent designs that minimize waste and maximize sustainability. It’s as if Mother Earth herself were an architect!
Hybrid Manufacturing Innovations
Armed with 3D printing, even the wildest designs come to life easily. But the real magic starts when hybrid manufacturing innovations join the party. It’s like getting the best of both worlds—think traditional construction’s durability and flexibility, plus 3D printing’s precision and speed. It’s an unstoppable combo that’ll revolutionize how we build our tomorrow.
Urban Mining and Waste-to-Material Technology
Once the stage of retail giants and fashion brands, upcycling is making its grand entrance into the construction arena. Rebranding itself as urban mining and waste-to-material technology, it’s the process of extracting valuable elements from waste to be recycled. Buildings, in this new era, won’t just be structures, but potential resource mines for future constructions. Mighty impressive, isn’t it?
To sum it all up, the future of circular 3D-printed construction lies in smarter design, better materials, and groundbreaking technologies. And as we move forward in this brave new world, we do so with the goal of less waste, more sustainability, and a better home for all on this little blue planet we call Earth.
2 Comments
Comments are closed.



[…] 3D and 4D printing are also part of the future plan. Imagine printing a material that changes whenever you need it to. This offers endless possibilities, especially for industries like medicine or construction. […]
[…] after printing, these parts are cut away and thrown out. They are useful while printing but become waste when […]